Narrow Band Imaging™ Technology
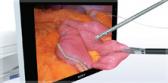
NBI™ Technology is an optical imaging technology that enhances the visibility of vessels and other tissue on the mucosal surface. NBI technology works by filtering the white light into specific light wavelengths that are absorbed by hemoglobin and penetrate only the surface of human tissue. As a result, with Narrow Band Imaging, capillaries on the mucosal surface are displayed in brown and veins in the submucosa are displayed in cyan on the monitor.2
Note: NBI™ technology is not intended to replace histopathology as means of diagnosis
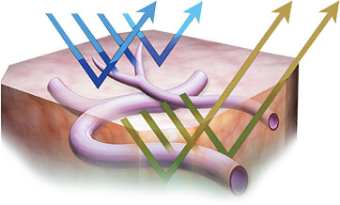
Upper GI Benefits
See Before You Sample – High-definition Narrow Band Imaging targets suspicious areas to biopsy for Barrett’s Esophagus.1

Lower GI Benefits
Suspect Before You Resect – High-definition Narrow Band Imaging can be used to assess the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps.2
Increased Adenoma Detection Rate – During randomized clinical trials, the use of Second Generation NBI Technology resulted in a statistically significant and clinically relevant increase in ADR.5
Suspect Before You Resect


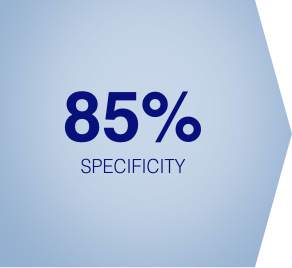




Detection Means Prevention
Increasing adenoma detection rate (ADR) may improve the ability to save lives. A 1% increase in ADR results in a 3% decrease in the risk of interval cancer and a 5% decrease in the risk of a fatal interval colorectal cancer.6
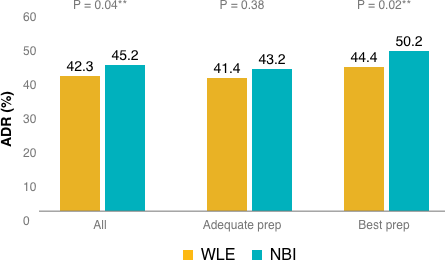
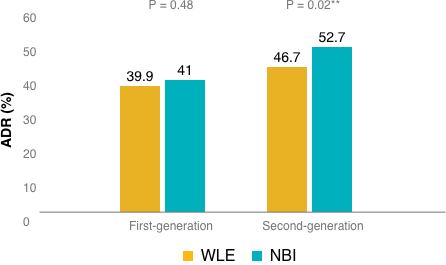
**A p-value less than 0.05 (typically ≤ 0.05) is statistically significant.
No significant difference was observed in the adequate bowel preparation group (OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.92–1.24; P = 0.38). However, the odds of detecting at least 1 adenoma in the “best” bowel preparation group was significantly higher with NBI compared to WLE (OR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.04–1.62; P = 0.02**).
(Figure 1)
The odds of detecting at least 1 adenoma with second-generation bright NBI* vs white light was significantly higher than with WLE (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05–1.56; P =0.02); however, this effect was not observed for first-generation NBI (OR, 1.06;95% CI, 0.91–1.24; P=0.48).
(Figure 2)
Don't leave biopsy to chance.
Better Interpretation Tool
HD NBI technology provides contrast, which may aid in the interpretation of mucosal morphology, vascular patterns, and blood vessel appearance in patients with Barrett’s esophagus.1
Less Time
HD NBI technology facilitates targeted biopsies in patients with Barrett’s esophagus, which can save valuable procedure time.1
Fewer Biopsies
Using HD NBI technology to target suspicious areas in Barrett’s.1
+ VIEW MORE IMAGES- VIEW FEWER IMAGES
Download our GI NBI Atlas

Olympus Continuum
LEARN MORE
1. Data held on file with Olympus (K100584) as of 07/02/2010
2. Data held on file with Olympus (K192793) as of 07/17/2020
3. ASGE Technology Committee et al. “ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations thresholds for adopting real-time imaging-assisted endoscopic targeted biopsy during endoscopic surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus.” Gastrointestinal endoscopy vol. 83,4 (2016): 684-98.e7. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.01.007
4. ASGE Technology Committee et al. “ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps.” Gastrointestinal endoscopy vol. 81,3 (2015): 502.e1-502.e16. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.12.022
5. Atkinson NSS, Ket S, Bassett P, et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:462–71.
6. Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, et al. Adenoma Detection Rate and Risk of Colorectal Cancer and Death. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1298-1306.
7. Data held on file with Olympus (K121959) as of 01/10/2013
* first-generation NBI technology refers to EVIS LUCERA SPECTRUM™ ENDOSCOPY SYSTEM or EXERA II™ ENDOSCOPY SYSTEM
* second generation NBI technology (bright) refers to EVIS LUCERA ELITE™ ENDOSCOPY SYSTEM or EVIS EXERA III™ ENDOSCOPY SYSTEM
Note: NBI is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
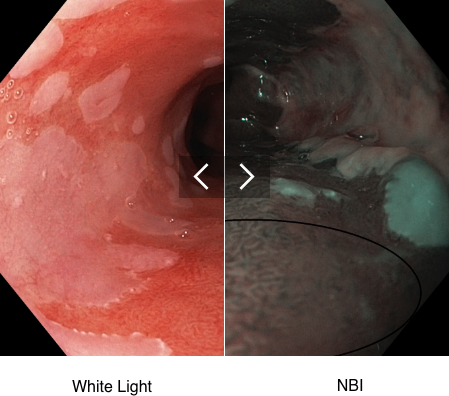
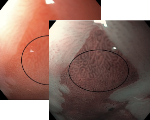
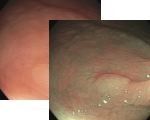
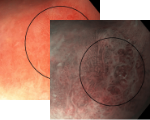
Esophagus - Barrett’s Esophagus Investigation
Regular Morpholgy shown under white light and NBI
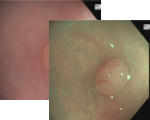
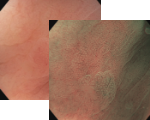
Esophagus - Barrett’s Esophagus Investigation
Regular Morpholgy shown under white light and NBI
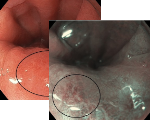
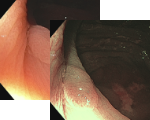
Esophagus - Barrett’s Esophagus Investigation
Vasculature appears slightly darker red than the surrounding tissue under white light. Unclear if regular or irregular morphology
However using NBI the Vascular morphology appears regular
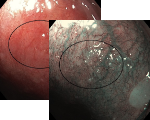
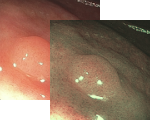
Esophagus - Barrett’s Esophagus Investigation
Under White morphology appears regular in the area denoted by the circle.
However under NBI the Mucosal morphology appears absent or irregular.
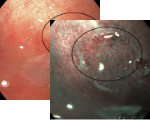
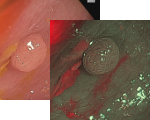
Esophagus - Barrett’s Esophagus Investigation
Under White there is irregularities in the area denoted by the circle.
This is supported by NBI as the Mucosal morphology appears absent or irregular.
NBI: Most likely prediction – NICE Type 1 – non adenoma
NBI: Most likely prediction – NICE Type 1 – non adenoma
NBI: Most likely prediction – NICE Type 1 – non adenoma
Most likely prediction – NICE Type 1 – non adenoma
Most likely prediction – NICE Type 1 – non adenoma
Most likely prediction – NICE Type 2–adenoma